

Calcium reacts with water and liberates hydrogen gas plus heat.Calcium is a chemically reactive metal so it is not found naturally, but it is always found as a compound with other elements.Chemical properties of CalciumĬhemical properties of calcium are mentioned below. Calcium salts can produce orange color, hence it is used in fireworks industries.Melting point of calcium is 842 ☌ and its boiling point is 1484 ☌.Calcium is a soft metal and it can be cut even with a kitchen knife.Calcium is a dull silvery grey colored soft alkaline earth metal.
/the-periodic-table--digital-illustration--73016803-598b218ec41244001024af78.jpg)
Physical properties of calcium are mentioned below. The physical and chemical properties of calcium element are mentioned below. Human body requires vitamin D to absorb the calcium from food.The requirement of calcium in the human body is fulfilled by eating (or drinking) calcium rich foods like yogurt, cheese, milk, spinach, etc.Calcium is an alkaline earth metal, so more calcium present in the soil results in alkaline soil (or soil having pH higher than 7). Calcium is also present in soil and it controls the pH level of soil.Out of all other metallic elements, the calcium element is the most abundant metallic element found in the human body.Calcium ions are also found dissolved in the sea water.Calcium is also the 5th most abundant element present in the human body.
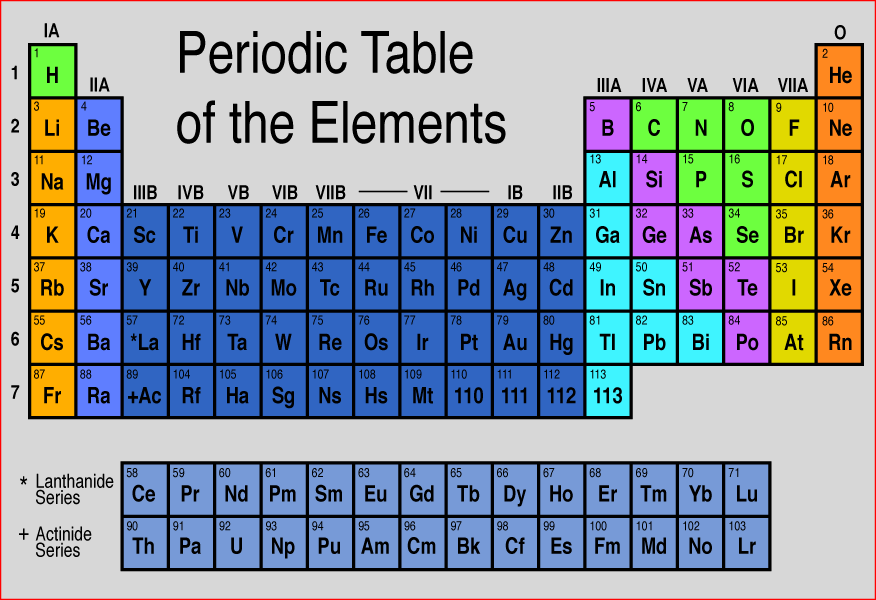 Calcium is the 5th most abundant element (by mass) found in the earth’s crust. Our teeth and bones contain calcium in it. Calcium is a very essential element for all living organisms. Interesting facts about calcium element are mentioned below. So the last electron of calcium enters the s-subshell or s-orbital. The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.įor example the electron configuration of calcium is 4s 2. How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements? Protons 20 Neutrons 20 Electrons 20 Symbol Ca Atomic massĢ, 8, 8, 2 Electronic configuration 4s 2 Atomic radiusĢ31 picometers (van der Waals radius) Valence electronsĢ 1st Ionization energy 6.113 eV ElectronegativityįCC (Face centered cubic) Melting point 1115 K or 842 ☌ or 1548 ☏ Boiling point 1757 K or 1484 ☌ or 2703 ☏ Density 1.55 g/cm 3 Main isotope 40Ca Who discovered Calcium and when?īefore knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question. Let’s dive right into it! Calcium Element (Ca) Information Appearanceĭull silvery grey color State (at STP) Solid Position in Periodic table So if you want to know anything about Calcium element, then this guide is for you. In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Calcium element in Periodic table.) This is a SUPER easy guide on Calcium element.
Calcium is the 5th most abundant element (by mass) found in the earth’s crust. Our teeth and bones contain calcium in it. Calcium is a very essential element for all living organisms. Interesting facts about calcium element are mentioned below. So the last electron of calcium enters the s-subshell or s-orbital. The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.įor example the electron configuration of calcium is 4s 2. How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements? Protons 20 Neutrons 20 Electrons 20 Symbol Ca Atomic massĢ, 8, 8, 2 Electronic configuration 4s 2 Atomic radiusĢ31 picometers (van der Waals radius) Valence electronsĢ 1st Ionization energy 6.113 eV ElectronegativityįCC (Face centered cubic) Melting point 1115 K or 842 ☌ or 1548 ☏ Boiling point 1757 K or 1484 ☌ or 2703 ☏ Density 1.55 g/cm 3 Main isotope 40Ca Who discovered Calcium and when?īefore knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question. Let’s dive right into it! Calcium Element (Ca) Information Appearanceĭull silvery grey color State (at STP) Solid Position in Periodic table So if you want to know anything about Calcium element, then this guide is for you. In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Calcium element in Periodic table.) This is a SUPER easy guide on Calcium element.


/the-periodic-table--digital-illustration--73016803-598b218ec41244001024af78.jpg)



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
