
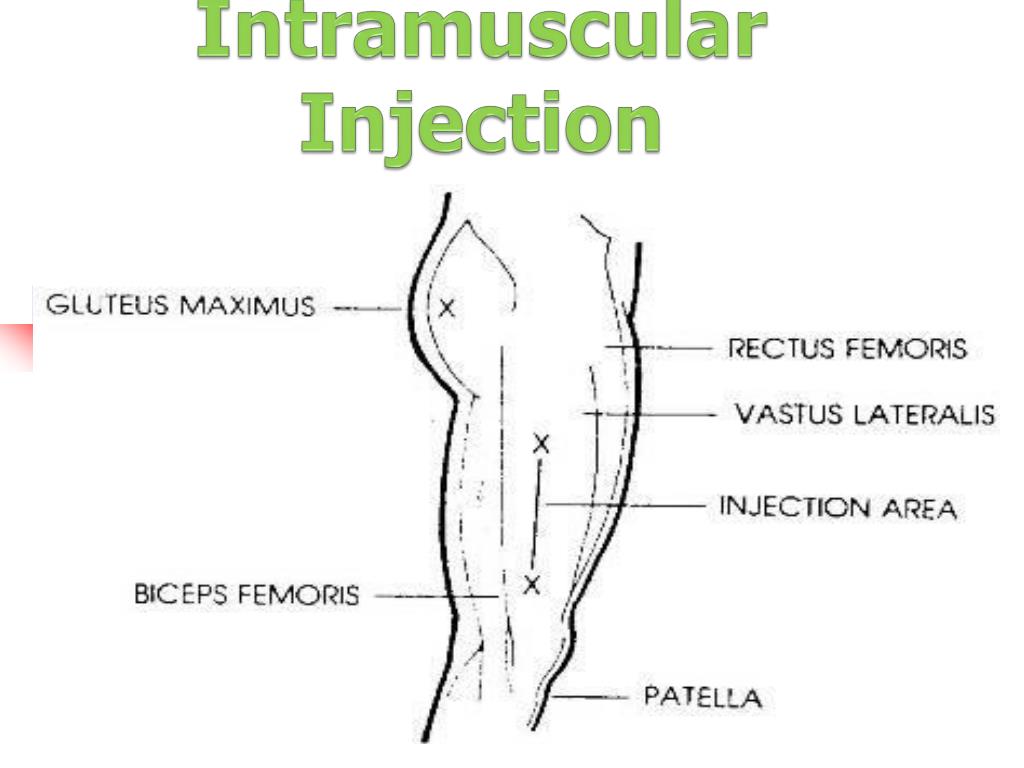
Anatomic SitesĪnatomic sites must be selected carefully for intramuscular injections and include the ventrogluteal, vastus lateralis, and the deltoid.

Research has found administering medications at 10 seconds per mL is an effective rate for IM injections, but always review the drug administration rate per pharmacy or manufacturer’s recommendations. Intramuscular injections are administered at a 90-degree angle. Medication fluid amounts up to 0.5-1 mL can be injected in one site in infants and children, whereas adults can tolerate 2-3 mL. Additionally, the muscle mass of infants and young children cannot tolerate large amounts of medication volume. However, if a patient is thin, a shorter needle length is used because there is less fat tissue to advance through to reach the muscle. The length of the needle must be long enough to pass through the subcutaneous tissue to reach the muscle, so needles up to 1.5 inches long may be selected. Muscle has an abundant blood supply that allows medications to be absorbed faster than the subcutaneous route.įactors that influence the choice of muscle to use for an intramuscular injection include the patient’s size, as well as the amount, viscosity, and type of medication. The intramuscular (IM) injection route is used to place medication in muscle tissue. 18.6 Administering Intramuscular Medications


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
